Vertigo is a symptom. Like fever.
It is not a diagnosis, but rather a symptom caused by some underlying medical issue.
It’s more than just feeling dizzy—it sensation that makes you feel like you or your surroundings are spinning. Vertigo can range from mild to severe, impacting your ability to perform everyday activities.
A vertigo attack can last anywhere from a few seconds to several hours. Overall recovery, depending on the condition, can take weeks or months. If left untreated, chronic vertigo can cause secondary issues like nerve or thoracic outlet type problems due to neck tightness and affect mental well-being, leading to anxiety and depression.
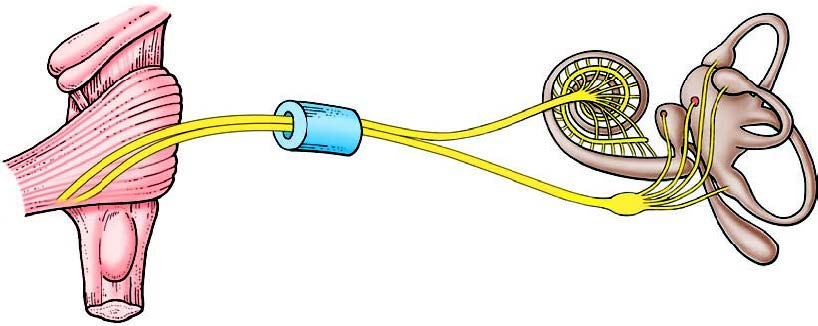
Vertigo is usually a result of an issue with the balancing system of the body. This is a combination of the inner ear- the nerve- and the brain. Below are the three most common causes of vertigo:
BPPV occurs when crystals in the inner ear become dislodged and move into the ear canals. These misplaced crystals disrupt fluid movement, sending incorrect signals to the brain about your body’s position.
Meniere’s disease is a chronic condition caused by an excess buildup of fluid in the inner ear, affecting both balance and hearing.
Vestibular neuritis is usually the most severe out of these 3. This occurs when the nerve in the inner ear becomes infected, disrupting communication between the ear and the brain. This is often caused by a viral infection.
Medications can help in the short term to reduce the intensity of the symptoms; Betahistine is most common.
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is one of the most effective non-medical treatments for vertigo. It includes:
Balance Training – Helps the brain adjust to dizziness overall.
Gaze Stabilization Exercises – Improves brain’s adaption to the dizziness and eye control to improve balance.
Vestibular Adaptation Techniques – Teaches the brain to compensate for the imbalance.
Positional Maneuvers (e.g., Epley Maneuver) – Helps relocate dislodged calcium crystals in BPPV cases.
Studies show that vestibular physiotherapy can significantly improve symptoms, helping patients regain confidence in movement.
Vertigo can be disruptive, but effective treatments do exist. These can help restore balance and reduce dizziness. If you’re struggling with vertigo symptoms, consulting a physiotherapist or ENT specialist can help you regain control and improve your quality of life.
If you’re experiencing persistent dizziness, please reach out to us; we’d be happy to help!

Arjun Patel, PT, MScPT, MCPA is an orthopedic, neuro, and vestibular physiotherapist. He is the director of Blue Space Clinic Physiotherapy and sees complex cases on a daily basis. He is also an adjunct lecturer at the faculty of medicine at University of Toronto.
To learn more about Arjun and our clinic, click here!